Hy this is Aman, and I welcome you again to my new blog, I hope you will find this useful and support my blog by sharing and commenting on it.
We provide you best articles related to Gaming, Technology, and Advanced Tech ( Soon we will providing you stock market and crypto-related blog )
So let's get started
Check out the previous blog about Steganography tools and techniques for beginners
What is DOS & DDOS?
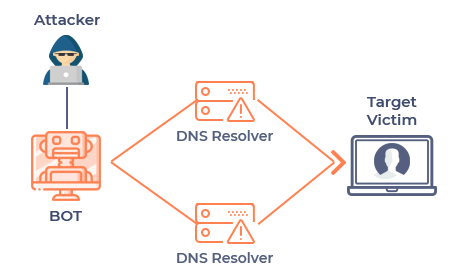
a denial of service could be in the form of:
Hijacking web-servers - Overloading ports with requests rendering them unusable
Denying wireless authentication - Denying any sort of service that is provided on the internet
NOTE: Attacks of such intent can be performed from a single machine
While single machine attacks are much easier to execute and monitor, they are also easy to detect and mitigate too.
To solve this issue, the attack could be executed from multiple devices spread across a wide area. ⇒ Such attacks are called Distributed Denial of Service or DDOS attacks.
How Does it Work?
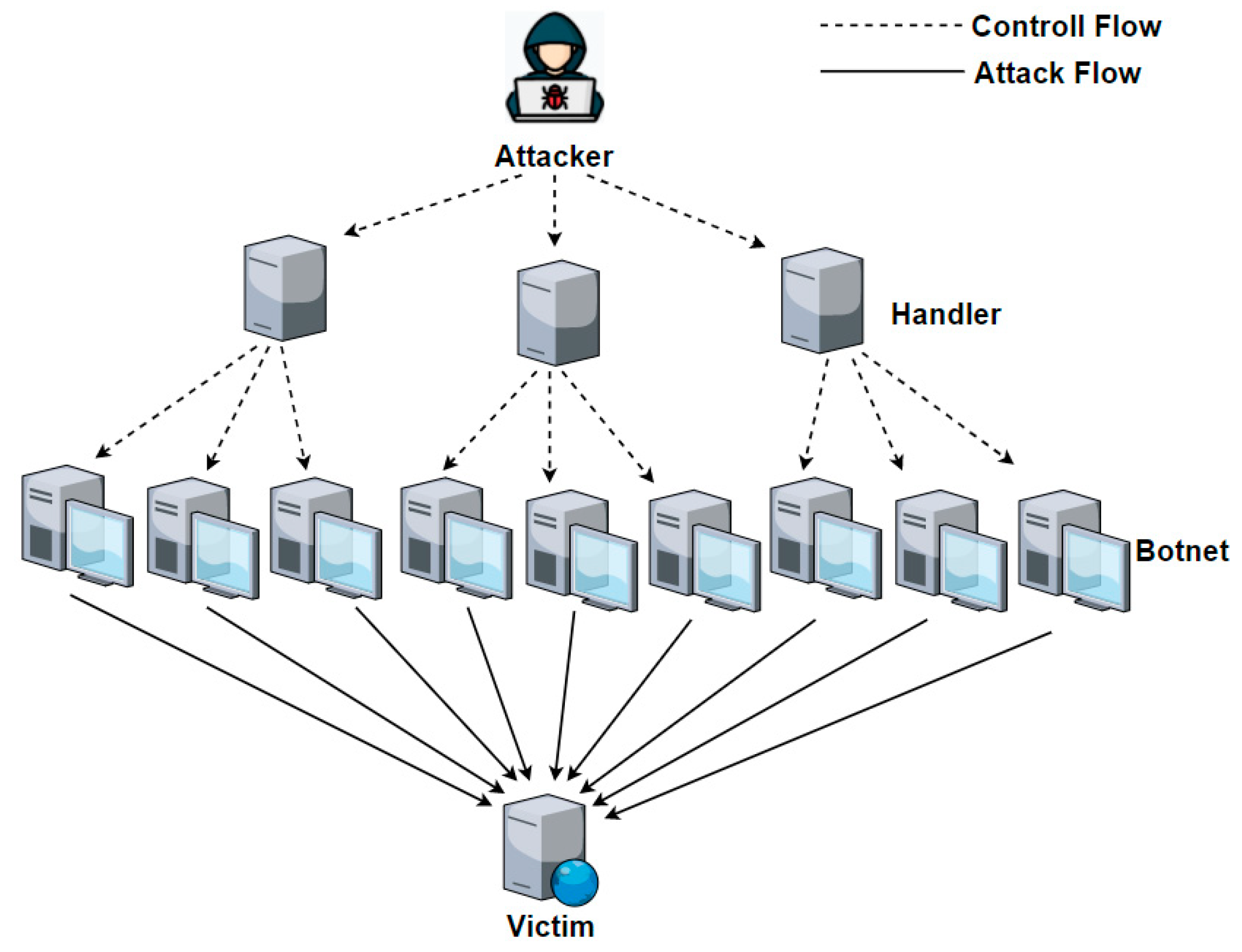
The goal of DOS Attack ⇒ making a certain service unavailable.
Since everything that is attacked is, in reality, running on a machine, the service can be made unavailable if the performance on the machine can be brought down.
This is the fundamental behind DOS and DDOS.
Some DOS attacks are executed by flooding servers with connection requests until the server is overloaded and is deemed useless.
Others are executed by sending unfragmented packets to a server which they are unable to handle
These methods when executed by a botnet, exponentially increase the amount of damage that they are doing, and their difficulty to mitigate increases in leaps and bounds.
Types of DDOS Attacks
- Ping of Death ⇒
In this, the attacker sends packets that are more than the max packet size when the packet fragments are added up.
max packet size is ⇒ 65,535 bytes
But in this attack, the attacker sends more than 65,535 bytes
Computers generally do not know what to do with such packets and end up freezing or sometimes completely crashing.
- Reflected Attacks ⇒
This type of attack is performed with the help of a botnet also called reflectors in this case
The attacker sends a host of innocent computers a connection request using a botnet, that looks like it came from the victim machine (this is done by spoofing the source in the packet header).
This makes the host of the computer send an acknowledgment to the victim's computer.
Since there are multiple such requests from different computers to the same machine, this overloads the computer and crashes it.
This type is also called a smurf attack.
- Mailbomb ⇒
Mailbomb attacks generally attack email servers.
In this type of attack instead of packets, oversized emails filled with random garbage values are sent to a targeted email server
This generally crashes the email server due to a sudden spike in load and renders them useless until fixed.
- Teardrop ⇒
In this type of attack, the fragmentation offset field of a packet is abused.
One of the fields in an IP header is the “fragment offset” field, indicating the starting position, or offset, of the data contained in a fragmented packet relative to the data in the original packet.
If the sum of the offset and size of one fragmented packet differs from that of the next fragmented packet, the packets overlap
When this happens, a server vulnerable to teardrop attacks is unable to reassemble the packets — resulting in a denial-of-service condition.
- Smurf ⇒
This type of attack uses large amounts of Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) ping traffic target at an Internet Broadcast Address.
The reply IP address is spoofed to that of the intended victim.
All the replies are sent to the victim instead of the IP used for the pings.
Since a single Internet Broadcast Address can support a maximum of 255 hosts, a smurf attack amplifies a single ping 255 times.
The effect of this is slowing down the network to a point where it is impossible to use it.
- SYN attack ⇒
SYN is a short form for Synchronize
This type of attack takes advantage of the three-way handshake to establish communication using TCP.
SYN attack works by flooding the victim with incomplete SYN messages.
This causes the victim machine to allocate memory resources that are never used and deny access to legitimate users.
- Buffer overflow ⇒
A buffer is a temporal storage location in RAM that is used to hold data so that the CPU can manipulate it before writing it back to the disc
Buffers have a size limit.
This type of attack loads the buffer with more data than it can hold.
This causes the buffer to overflow and corrupt the data it holds.
An example of a buffer overflow is sending emails with file names that have 256 characters.
So this is enough for today guys, hope you like it
Check out our more posts -
Steganography tools and techniques
Digital Forensics in cyber security
Cryptography in cyber security
Thanks for reading,
To your success,
Aman Yadav
You can also connect with us on our social profile mentioned below -
- Instagram - https://www.instagram.com/its_aman_yadav/
- Twitter - https://twitter.com/its_aman_yadav
- Facebook - https://www.facebook.com/itsamansays
- Linkedin - https://www.linkedin.com/in/aman-yadav-b3a81120a/
- Youtube - https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCbX9mKeH4vjUX1in1v3Y-Lg
#ddos #botnet #ps #ddosattack #botnets #bo #booter #vpn #botnetspots #botnetsetup #kalilinux #botnetforsale #qbot #botnetseller #xbox #gta #cybersecurity #ovh #anonymous #mirai #botnetspotsforsale #fortnite #online #linux #cyber #bhfyp #love #amansays #itsamanyadav

0 Comments